Simulations of the welding process for butt and tee joints using finite element analyses are presented. The base metal is aluminum alloy 2519-T87 and the filler material is alloy 2319. The simulations are performed with the commercial software SYSWELD+®, which includes moving heat sources, material deposit, metallurgy of binary aluminum, temperature dependent material properties, metal plasticity and elasticity, transient heat transfer and mechanical analyses. One-way thermo-mechanical coupling is assumed, which means that the thermal analysis is completed first, followed by a separate mechanical analysis based on the thermal history.

The residual stress state from a three-dimensional analysis of the butt joint is compared to previously published results. For the quasi-steady state analysis the maximum residual longitudinal normal stress was within 3.6% of published data, and for a fully transient analysis this maximum stress was within 13% of the published result. The tee section requires two weld passes, and both a fully three-dimensional (3-D) and a 3-D to 2-D solid-shell finite elements model were employed. Using the quasi-steady state procedure for the tee, the maximum residual stresses were found to be 90-100% of the room-temperature yield strength. However, the longitudinal normal stress in the first weld bead was compressive, while the stress component was tensile in the second weld bead. To investigate this effect a fully transient analysis of the tee joint was attempted, but the excessive computer times prevented a resolution of the longitudinal residual stress discrepancy found in the quasi-steady state analysis. To reduce computer times for the tee, a model containing both solid and shell elements was attempted. Unfortunately, the mechanical analysis did not converge, which appears to be due to the transition elements used in this coupled solid-shell model.
Welding simulations to predict residual stress states require three-dimensional analysis in the vicinity of the joint and these analyses are computationally intensive and difficult. Although the state of the art in welding simulations using finite elements has advanced, it does not appear at this time that such simulations are effective for parametric studies, much less to include in an optimization algorithm.
پروژه شبیه سازی جوشکاری و اتصال آلیاژهای آلومینیوم به روش آنالیز اجزای محدود (Welding Simulations of Aluminum Alloy Joints by Finite Element Analysis)، توسط Justin D. Francis از انستیتو پلی تکنیک ویرجینیا در سال 2002 نگارش شده است. پروژه مشتمل بر 7 فصل، 242 صفحه، به زبان انگلیسی، تایپ شده، به همراه تصاویر، با فرمت pdf به ترتیب زیر گردآوری شده است:
Chapter 1: Utilizing welding simulations in vehicle structural design
- Finite Element Analysis in Vehicle Design
- Global/Local Optimization
- Weld Joint Model in Phase I
- Objective
- Summary of Subsequent Chapters
Chapter 2: Processes and Metallurgy of Welding Aluminum Alloy
- Gas Metal Arc Welding Aluminum
- Weld Quality
- Procedures
- Weld Residual Stresses
- Precipitation Hardening of Aluminum
- Solution Heat Treatment
- Precipitation Heat Treatment
- Hardening Mechanism
- SYSWELD Metallurgical Model for Precipitate Dissolution Kinetics
Chapter 3: Finite Element Analyses of Welding
- Two D versus 3-D Finite Element Models
- Thermal, Mechanical, and Metallurgical Analyses
- Modeling the Weld Arc
- Weld Metal Deposition
- Material Model
- Boundary Heat Loss/Radiation and Convection
Chapter 4: Energy and Constitutive Equations in Welding Simulations
- Heat Flow in Welding
- Conservation of Energy
- Fourier Law of Heat Conduction
- Heat Conduction Equation
- Initial and Boundary Conditions
- Moving Heat Sources and Pseudo-Steady State
- Thermo elastic-Plastic Stress Analysis
- Fundamental Assumptions
- Fundamental difference between elastic and plastic deformation of solids
- Idealized uniaxial stress-strain curves
- von Mises Yield Criterion
- Strain Hardening
Chapter 5: SYSWELD Models of the Butt and Tee Joints
- SYSWELD Capabilities
- SYSWELD Analysis Procedure
- SYSWELD Analysis Preparation
- Finite Element Meshes for the Butt and Tee Joints
- Mesh Size and Time Step Relationship
- Aluminum 2519 and 2319 Material Properties
- Thermal Boundary Conditions
- Mechanical Boundary Conditions
- Specified Metallurgical Parameters
- Specified Weld Arc Model Parameters
- Element Activation/De-activation
Chapter 6: Results and Discussion
- Butt-weld Analysis
- Moving Reference Frame Analysis
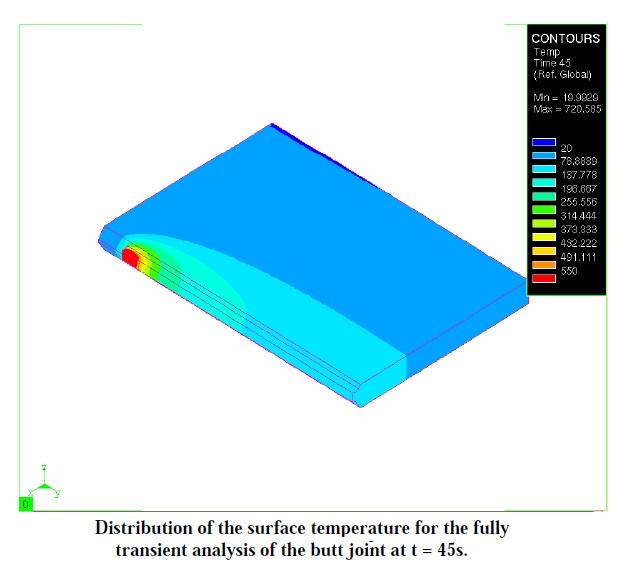
- Fully Transient Analysis
- Tee Section Analysis
- Tee Section “Moving Reference Frame” Analysis
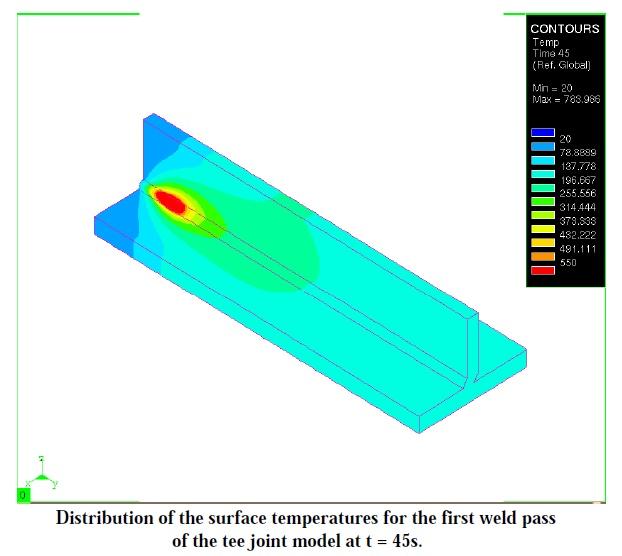
- Tee Section Fully Transient Analysis
- Solid-Shell Coupled Tee Section Analysis
Chapter 7: Concluding Remarks
- Summary
- Butt-weld Analysis Results
- Tee Section Analysis Results
- Computation Times and Disk Storage
- Conclusions
Appendix A: Butt-weld Moving Reference Frame Analysis Input Files
- THERM1.DAT
- THERM2.DAT
- COOL.DAT
- MECH1.DAT
- MECH2.DAT
- MECH3.DAT
- METALLURGY.DAT
Appendix B: Tee Section Transient Analysis Input Files
- THERM1.DAT
- THERM2.DAT
- MECH1.DAT
- MECH2.DAT
- METALLURGY.DAT
جهت دانلود پروژه شبیه سازی جوشکاری و اتصال آلیاژهای آلومینیوم به روش آنالیز اجزای محدود (Welding Simulations of Aluminum Alloy Joints by Finite Element Analysis)، بر لینک زیر کلیک نمایید:
:: موضوعات مرتبط:
جوشکاری،
پروژه،
،


















 آمار
وبلاگ:
آمار
وبلاگ: